Going back to my early days in data science, I was so excited to get my hands on raw data, curate it and feed it to my machine learning model! I felt like I was hacking the world - especially when I was getting unrealistically high “accuracy” metrics!
Little did I know that there was still a way to go to reach success.
Introduction
Machine learning models are developed to predict a target variable within a static environment. Once the models are productionised and the outputs are used to drive business decisions, the environment they are used in is no longer static. Meaning that over time, statistical properties of the predicted variable and those used to make the prediction are very likely to change. This change can lead to the model performance deteriorating over time, meaning it’s important to continue to monitor the model and identify when these properties do begin to drift.
Model monitor is something usually left in chance and apart from a few technical giants of the industry, this is due to limited experience with real-life machine learning applications.
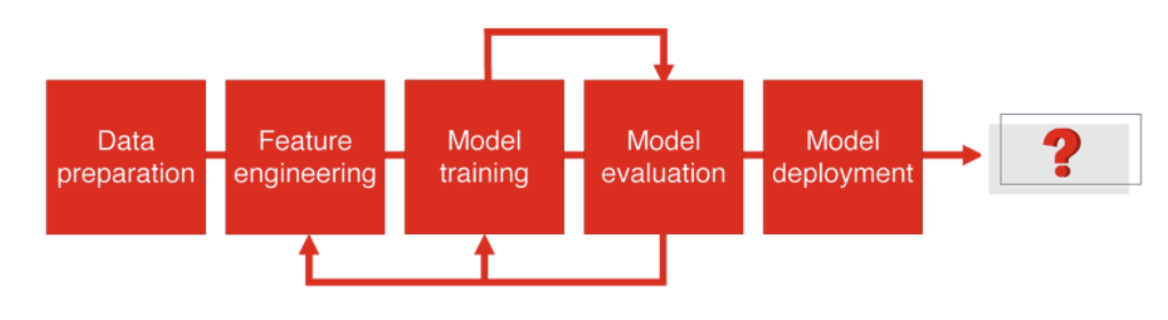
(Source: https://evidentlyai.com/blog/machine-learning-monitoring-what-it-is-and-how-it-differs)
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of model monitoring and the disastrous consequences model drift can have in real life.
- Instacart’s model’s accuracy predicting item availability at stores dropped from 93% to 61% due to a drastic shift in shopping habits.
Instacart keeping up with the coronavirus pandemic - Image classification models had to learn the new normal: a family at home in front of laptops can now mean “work,” not “leisure.”
AI is struggling to adjust to 2020 - Article
Model drift
Model drift (also known as Model Decay) is the term used to describe how a machine learning model loses its predictive power over time. It’s a concept that tends to slowly appear within models over time and if not detected, can have a detrimental effect on the performance. A sign that can reveal drift can be the ultimate measure is the model quality metric. It can be accuracy, mean error rate, or some downstream business KPI, such as click-through rate.
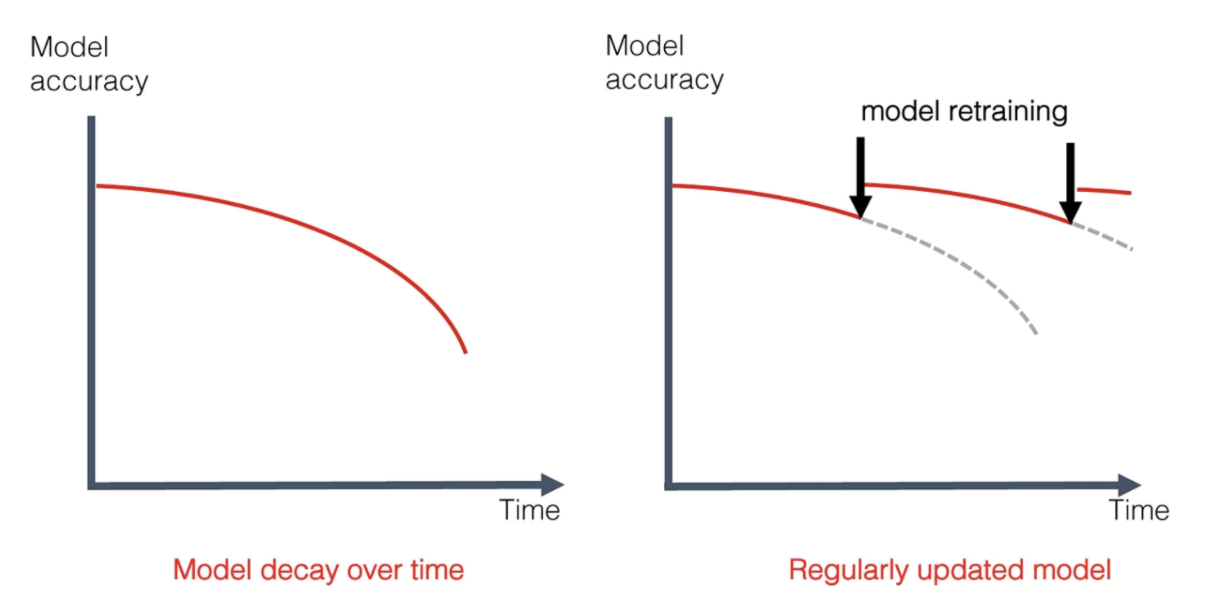
Model drift can be caused by a number of reasons, the two key being concept drift and data drift.
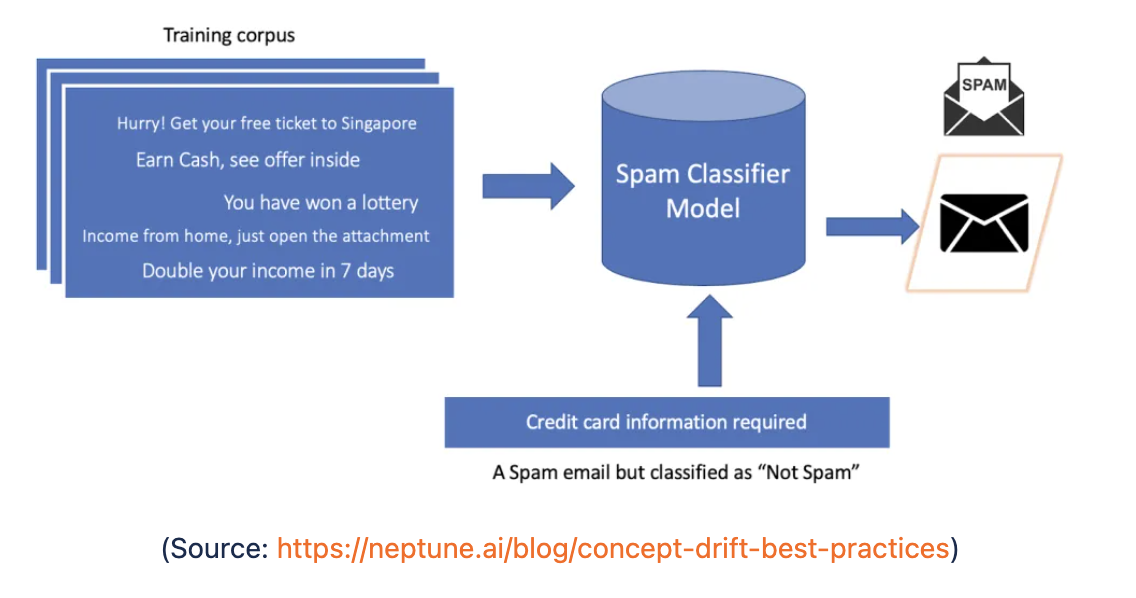
The below image shows a simple process for a spam mail classifier. The model learns the relationship between the input variables (key spam words) and the target variable and then uses this relationship to determine if future emails are classed as spam or not spam. However over time spam emails may change, senders may start to use different keywords to get around spam detectors or the general content of the emails may change. This is going to lead to the model deteriorating if left without re-training on new data.
Concept Drift
Concept drift is a phenomenon where the statistical properties of the target variable have changed over time. In other words, concept drift occurs when the patterns the model learned no longer hold.
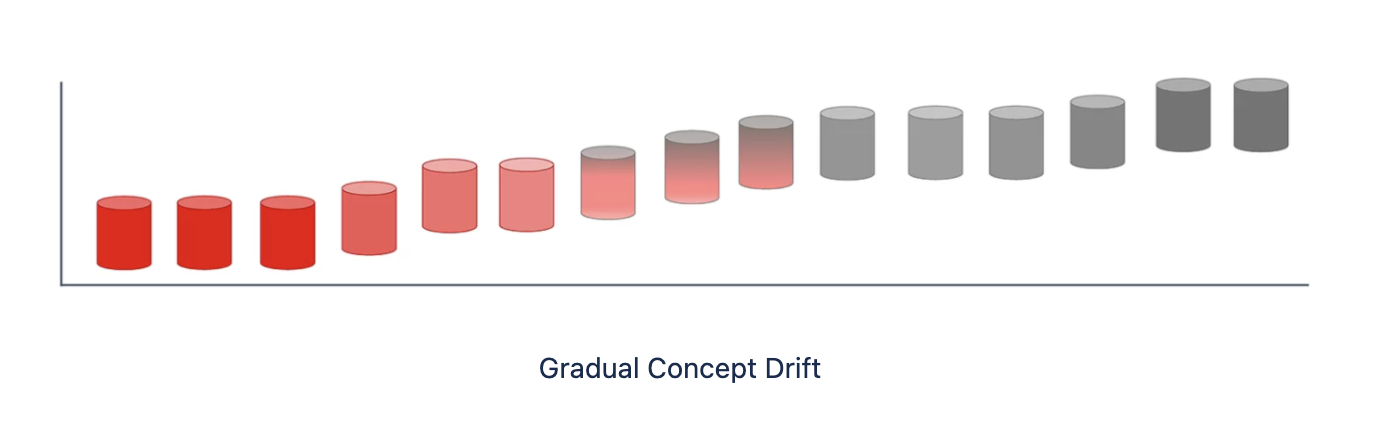
Gradual Concept Drift
Gradual concept drift is the most common and expected drift that might occur over time. Gradual concept drift suggests that external factors affect the quality of the predictions. Such a change leads to the model growing old and Its quality decline gradually.
Sudden Concept Drift
External changes might be more sudden or drastic. The COVID-19 pandemic is a perfect example where the changes in behavior have shifted almost overnight. Sudden concept drift affected all sorts of models, even otherwise “stable” ones.
Data Drift
Data drift is a similar phenomenon to concept drift, but in this case, the statistical properties of the independent variables have changed. In other words, the input data has changed and the distribution of the variables is meaningfully different.
Data drift can be caused by a number of reasons.
- Natural drift in the input data, such as airline demand changes with seasons.
- Data quality issues, input pipeline may be broken
- Changes in upstream processes such as competitor data extraction have moved to EUR rather than GBP
- Change in the relation between features, or covariate shift.
How to detect drift
Both concept and data drift are related to the statistical change in data, therefore the best approach to detect them is by monitoring the variable’s statistical properties, model predictions, and correlations between factors.
This could be through dashboards showing changes over time or including calculations directly into the production system that will raise alerts if unexpected changes appear.
An alerting tool such as Evidently AI or, alternatively, Prometheus and a python library called scikit-multiflow could be used.
How to overcome drift
With the current environment used for training, a machine learning model needs to constantly be monitored in order to detect drift and take actions to overcome drift. Sooner or later, even the most accurate and carefully tested solutions will start to degrade. Therefore, drift visibility and monitor is a critical part of the model development lifecycle.
In case of quality drop due to model drift, there are two main options that can help models overcome drift
- One simple option to overcome model drift is with training. The pipeline could include a system that retrains the model after a fixed period of time or when drift has been identified.
- Model decay can be prevented by doing a step back into the feature engineering and research phase to issue a model remake.
You can find my personal PoC (Proof of Concept) jupyter notebook on how to receive an alert in case a model is experiencing model and data drift:
PoC Model Monitor - Model & Data Drift
Idea inspired by:
Evidently tutorial - MLOps Example
Resources
- https://www.trainindatablog.com/testing-and-monitoring-machine-learning-model-deployments/
- https://databricks.com/building-and-deploying-machine-learning-models
- https://github.com/visenger/awesome-mlops
- https://www.kdnuggets.com/2021/01/mlops-model-monitoring-101.html
- https://www.explorium.ai/blog/understanding-and-handling-data-and-concept-drift/
- https://github.com/evidentlyai/evidently
- https://evidentlyai.com/blog
- https://evidentlyai.com/blog/machine-learning-monitoring-data-and-concept-drift