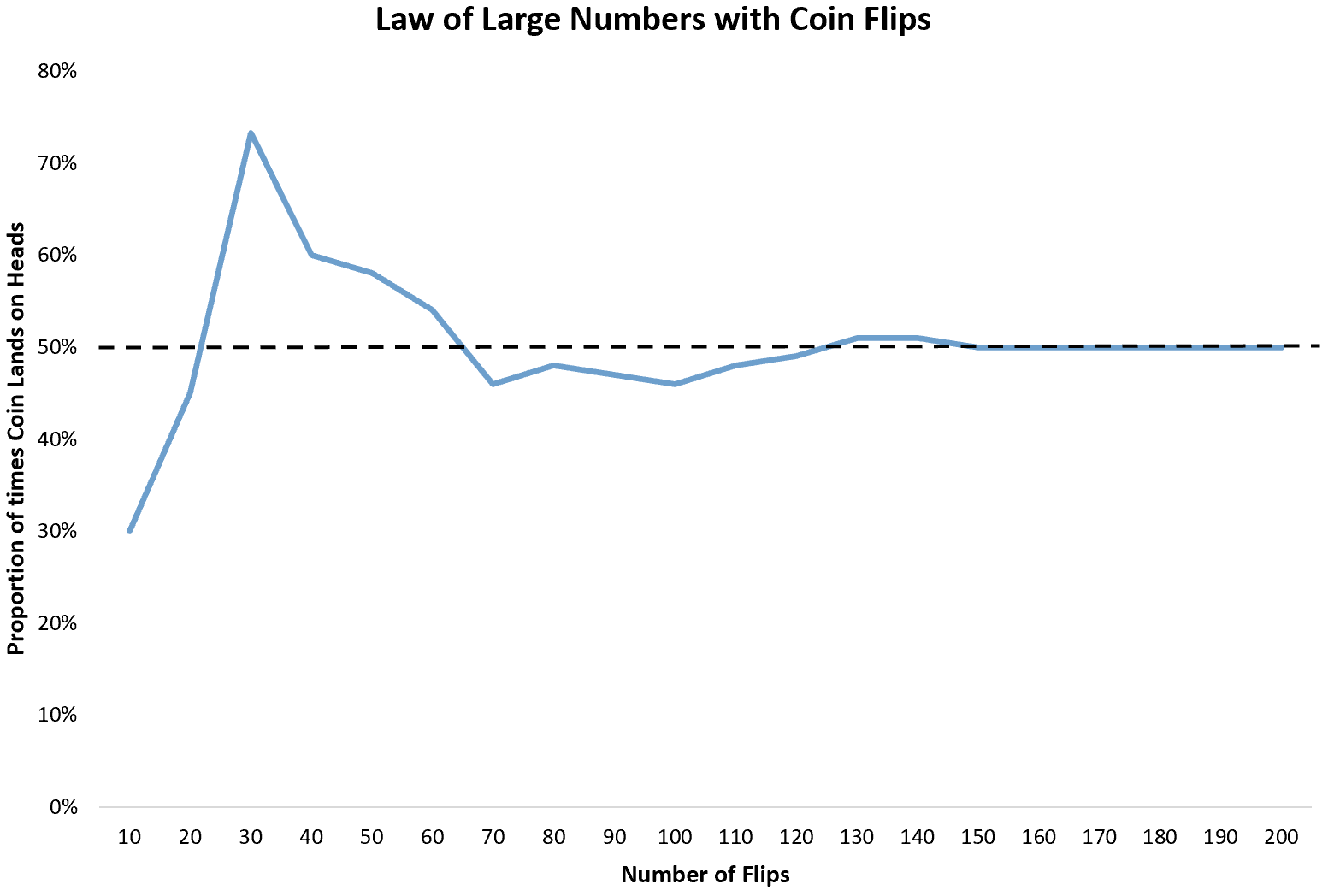
The law of large numbers is a statistical theorem that states that as the number of identically distributed, randomly generated variables increases, their sample mean approaches their theoretical mean.
In layman terms
In simpler terms, as the sample size becomes larger, the sample mean gets closer to the expected value.
Usefulness
The law of large numbers is useful in hypothesis testing because it helps to reduce the impact of sampling error. Sampling error is the difference between the sample mean and the true population mean, which is due to the fact that we are only observing a small subset of the population.
The law of large numbers suggests that as the sample size increases, the sample mean will converge towards the true population mean, and the sampling error will decrease.
Thus, by increasing the sample size, we can reduce the impact of sampling error and increase the statistical power of our hypothesis test. This means we are more likely to detect a true difference between the two groups, and less likely to mistakenly conclude that there is no difference when one actually exists.